Metasploit Tutorial 1
September 27, 2024
The Metasploit project is a powerful, open-source platform designed for penetration testing, helping security experts discover and exploit vulnerabilities in systems. It all started back in 2003 when H.D. Moore developed Metasploit as a flexible network tool.
Since then, Metasploit has grown significantly, and on October 21, 2009, it was acquired by Rapid7, further expanding its capabilities and reach.
Today, Metasploit is an essential resource for security professionals and IT teams alike. It assists in identifying security weaknesses, confirming that vulnerabilities have been properly mitigated, and conducting in-depth, expert-led security assessments.
The project encompasses several sub-projects, including the well-known Metasploit Framework and its commercial editions: Metasploit Pro, Express, Community, and Nexpose Ultimate, each catering to different needs and environments.
Supported Operating Systems (as of 2025):
- Windows Server 2008, Server 2012, Windows Server 2025
- Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows 11
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.10, 6.5, 7.1 or later
- Ubuntu Linux 14.04, 16.04 LTS, and newer releases (e.g., 20.04, 22.04)
Basic Terms of Metasploit
Vulnerability: A weakness exploited by an attacker to perform unauthorized actions with a system.
Exploit: Code or commands that take advantage of a vulnerability to trigger unintended behavior like unauthorized access.
Payload: The component that performs the malicious action (e.g., deleting data or sending spam).
Auxiliary: Modules for scanning, sniffing, fuzzing. Not for shells but useful for brute force and vulnerability scanning.
Post: Modules used on compromised machines to gather evidence or pivot.
Encoders: Help ensure payloads reach their destination, often used to evade AV.
Nops: Used to maintain consistent payload size.
A Cheat Sheet of Basic Commands
Start Metasploit
msfconsole
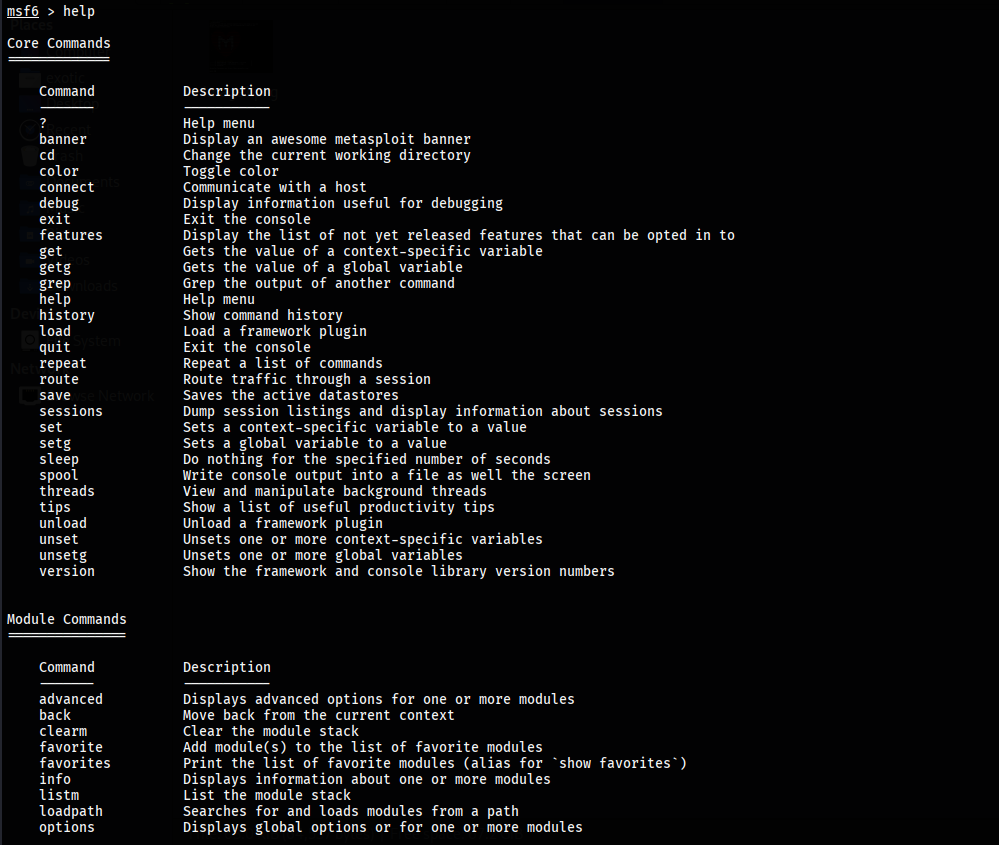
After starting the Metasploit framework, we can check for the basic commands by using “help” command.
msf > helpCore Commands:
? / help: Display the summary of commands that can be used in msfconsole.
banner: Change and display banner in msfconsole.
cd: Change the current working directory.
color: Enable or disable the color output of Metasploit. It has 3 options “true”, “false” and auto.
connect: netcat like function to connect to a host machine build into msfconsole.
exit: Exit the Metasploit console.
get: Gets the value of a context-specific variable
getg: Gets the value of global variable
grep: It matches a given pattern from the output of another msfconsole command
history: Shows command that are previously used in Metasploit
irb: Opens a live ruby interactive shell
load: Loads a Metasploit plugin
quit: Exit the Metasploit console
route: It allows you to route sockets through a session or ‘comm’, providing basic pivoting capabilities
save: This command allows you to save your current environment and settings
sessions: This command allows you to list, interact, and kill spawned sessions
set: This command allows you to configure Framework options and parameters for the current module that is selected on the console.
setg: This command is used to set global variables within msfconsole
sleep: Do nothing for the specified number of seconds
spool: It allows a user to save the output of Metasploit console to a specified file
threads: View and manipulate background threads
unload: unloads a previously loaded plugin and removes any extended commands
unset: It removes a parameter previously configured with set
unsetg: It removes a global variable inside msfconsole
version: Show the framework and console library version numbers
Module Commands:
advanced: It is used to further fine-tune a module, ‘show advanced’ displays a more advanced option for a module.
back: Once you have finished working with a particular module, or if you inadvertently select the wrong module, you can issue the back command to move out of the current context.
info: It provides detailed information about a particular module including all options, targets, and other information.
loadpath: It loads a third-party module tree for the path.
options: It shows you the available parameters for an exploit.
popm: It pops the pushed module from the top of the module stack.
previous: It sets the previously loaded module as the current module.
pushm: This command pushes the current module on to the stack.
reload_all: It reloads all modules from all defined module paths.
search: It searchers module names and descriptions
show: This command displays modules of a given type, or display all modules.
use: It is used to select a particular module.
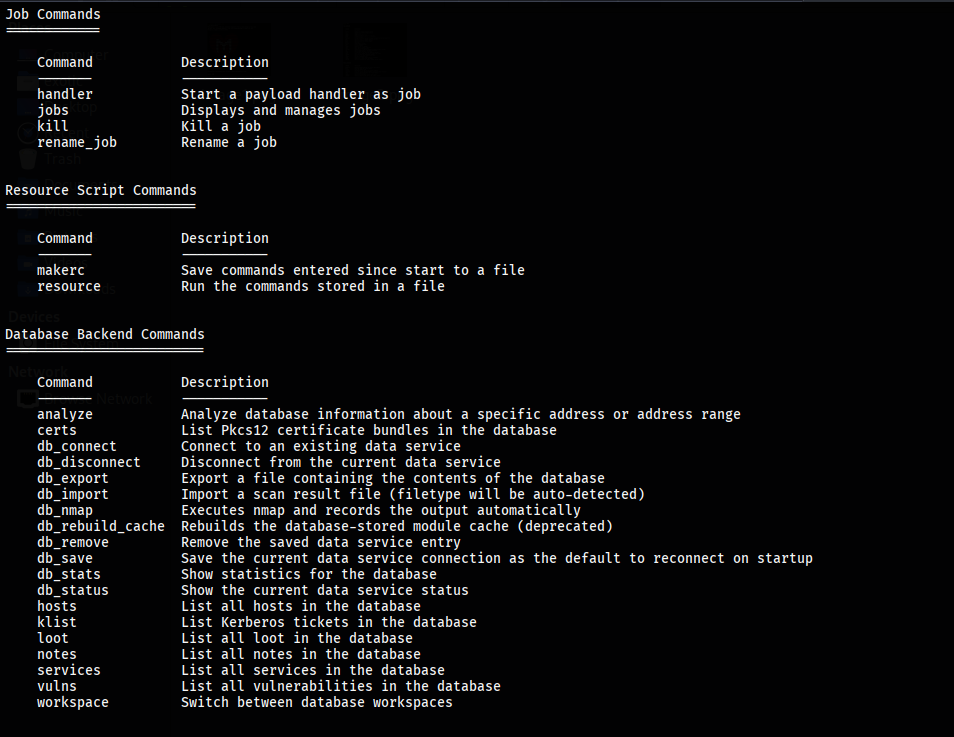
Job Commands:
handler: It starts a payload handler in the background.
jobs: It is used to list jobs running in the background and terminate them.
kill: It kills any running job.
rename_job: It is used to rename a job.
Resource Script Commands:
makerc: It saves commands entered to a specified rc file.
resource: It runs all the command stored in the rc file.
Developer Commands:
edit: This command is used to edit the currently selected module.
log: It displays framework.log starting from the bottom.
reload_lib: This command is used to reload one or more library files from specified paths.
Database Backend Commands:
db_connect: It is used to connect to an existing database.
db_disconnect: It is used to disconnect from the current database instance.
db_export: It is used to export a file containing the contents of the database.
db_import: It is used to import a scan result file.
db_rebuild_cache: It is used to rebuild the database-stored module cache.
db_status: It shows the name of the currently connected database.
hosts: It lists all hosts in the database.
loot: It lists all loot in the database.
notes: It lists all notes in the database.
services: It lists all services in the database.
vulns: It lists all vulnerabilities in the database.
workspace: It helps to switch between database workspaces.
To view every payload available in the Metasploit framework, execute the command show payloads. This will display a complete list of payloads sorted alphabetically.
msf > show payloads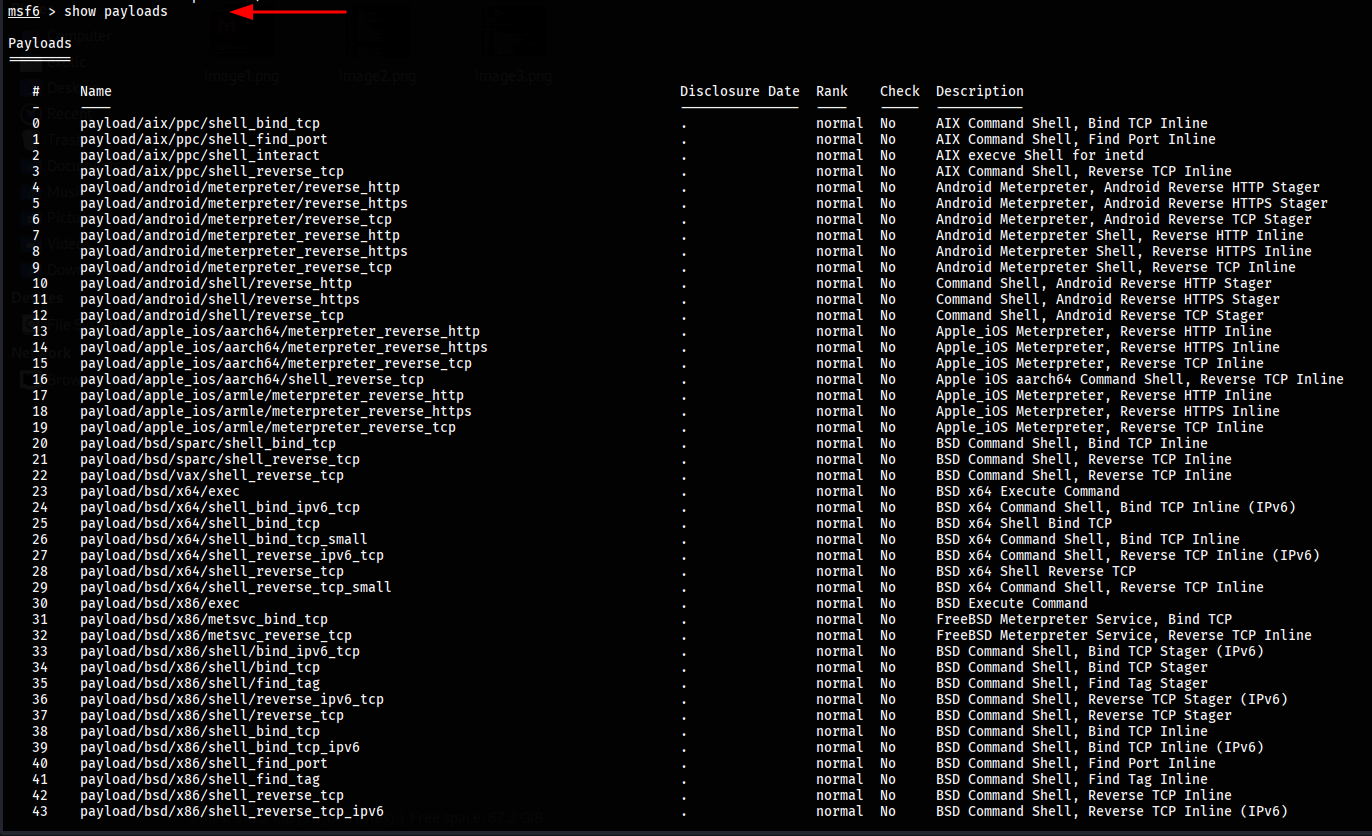
To view all exploits available in the Metasploit framework, use the command show exploits. This command lists all exploits alphabetically, along with their disclosure date and rank, which ranges from “Excellent” to “Average”.
msf > show exploits
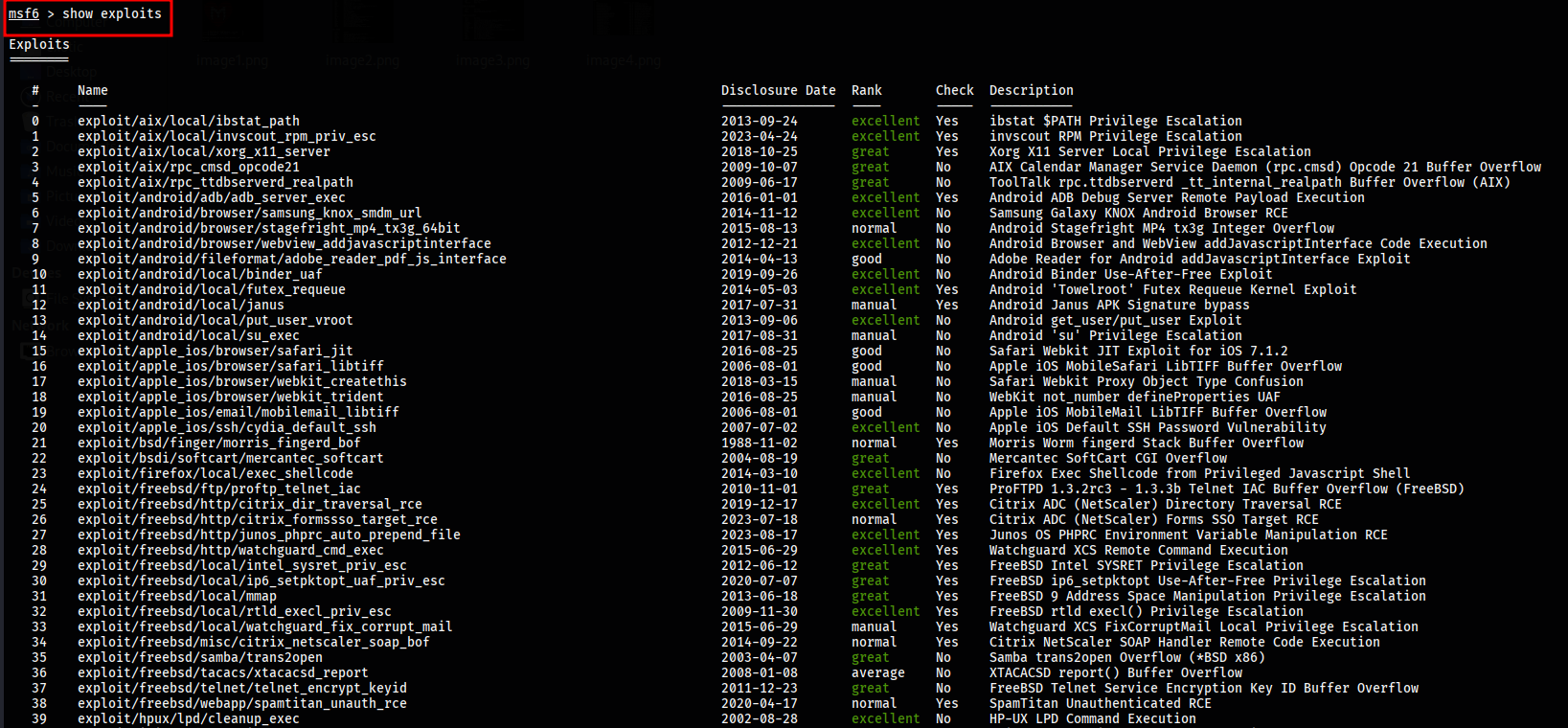
To view all auxiliary modules available in the Metasploit framework, use the command show auxiliary. Auxiliary modules include scanners, denial of service tools, fuzzers, and more.
msf > show auxiliary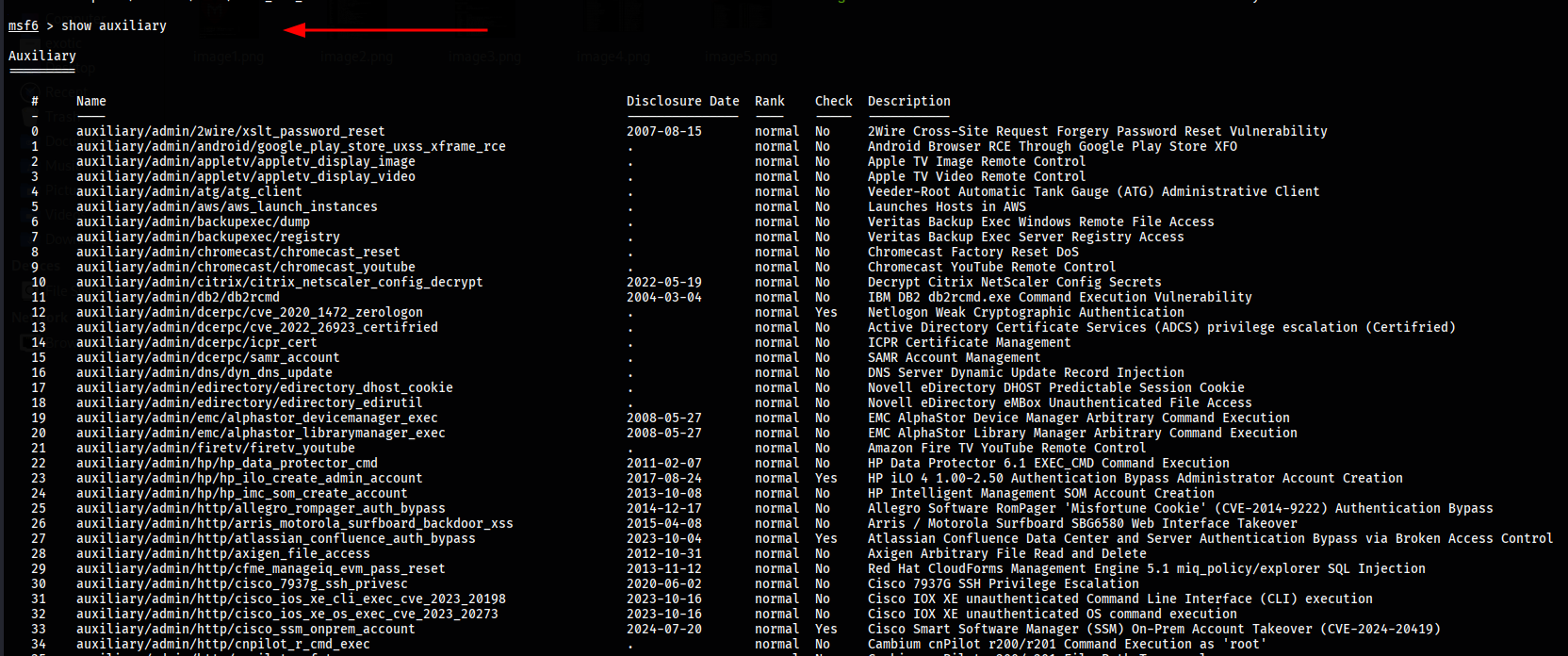
To list all available post-exploitation modules in the Metasploit framework, use the command show post. Post modules are designed for actions after exploitation, such as gathering evidence, extracting credentials, or pivoting deeper into a compromised network.
msf > show post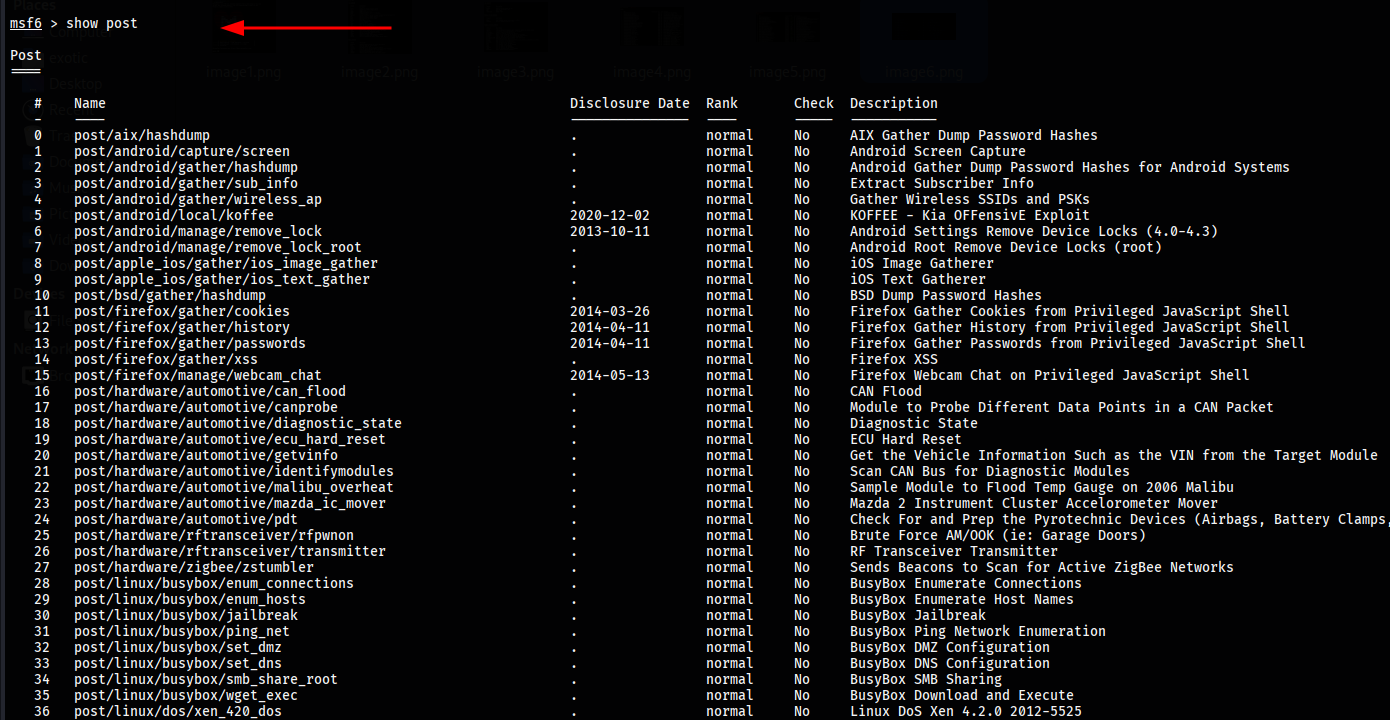
To display all encoders available in the Metasploit framework, use the command show encoder. Encoders are used to obfuscate modules in order to evade detection by security mechanisms like antivirus or firewalls.
Encoders modify the payload’s code to avoid signature-based detection without changing its functionality. They are particularly useful when your payload is being flagged or blocked by security software.
msf > show encoders
To display all the NOP generators available in the Metasploit framework, use the command show nops. NOPs (No Operation instructions) are used to maintain a consistent payload size during exploit attempts, helping to improve reliability.
msf > show nops
- Younes